CATHODIC PROTECTION
Corrosion monitoring and cathodic corrosion protection (CP) are the core competencies of CATÓDICA. An electrochemical process occurs during corrosion of the reinforcement in concrete, and the rate of corrosion is determined by this process.
Installing a cathodic protection system reduces corrosion to a non-critical level. By applying an external electrical current, the reinforcement steel is polarized from an anode to a cathode, stopping the anodic (corrosive) reaction.
To maintain this polarization over the structure’s life span, consistent adjustment and maintenance is essential – ensuring compliance with one of the protection criteria according to DIN EN ISO 12696. System conditions and protection performance are documented in annual reports.

CP Systems
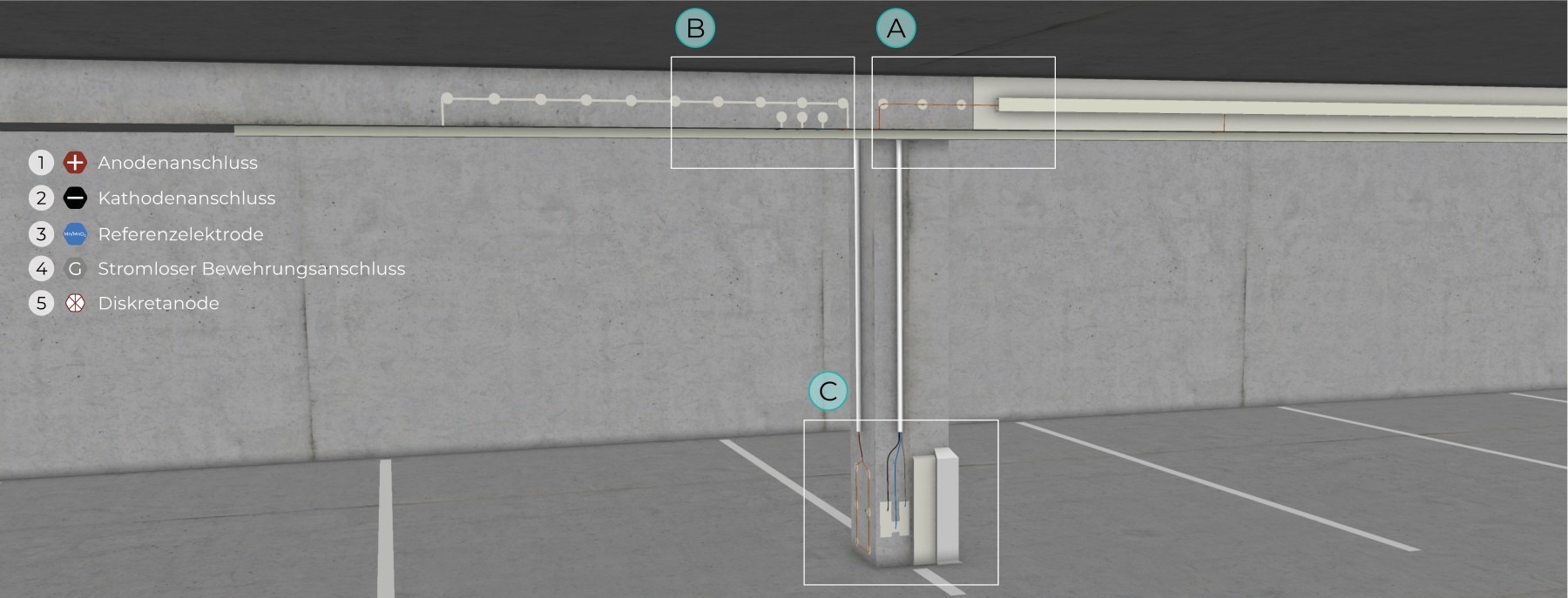
In general, Ti/MMO anodes can be used in the form of meshes, ribbons, or discrete (rod-type) anodes, as well as conductive coatings applied to floors, wall and column bases, frames, beams, or secondary structural elements. These anodes are classified as impressed current anodes, also known as externally powered systems. In special applications, galvanic anodes—such as zinc mesh systems—may also be used.
Ti/MMO anodes are used in accordance with the German technical rule for the Maintenance of concrete structures (TR Maintenance). Conductive coatings and galvanic anodes require project-related approval. The different systems vary in terms of performance capacity and areas of application.
All types of anodes are described in DIN EN ISO 12696 and can be designed, installed, and maintained by qualified CP specialists in accordance with DIN EN ISO 15257.
Ti/MMO anodes in the form of ribbons, available in various widths and corresponding power capacities, can be used in a wide range of components and in diverse applications. Their geometric shape allows for high design flexibility.
In 2004, the second multi-storey car park in Germany was rehabilitated using cathodic protection (CP). The column bases were protected using titanium ribbon and mesh anodes. The system is still in operation today. More information can be found in our project portfolio.
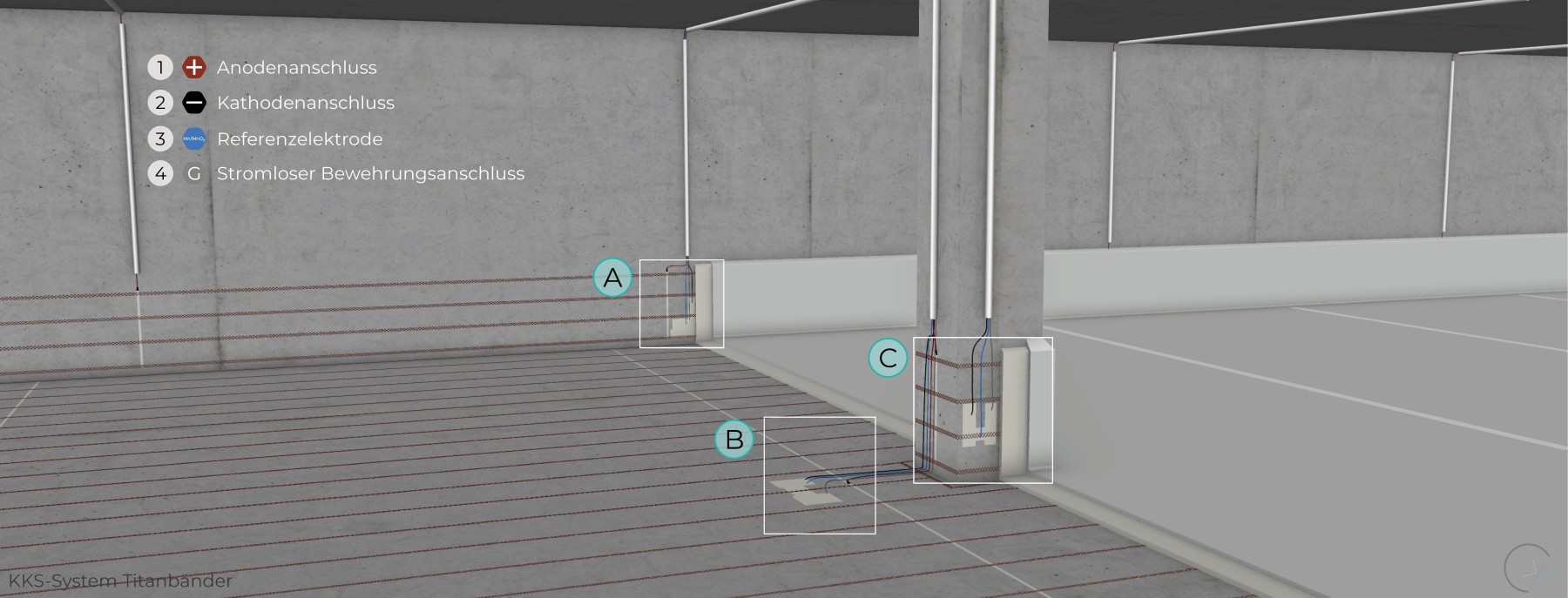
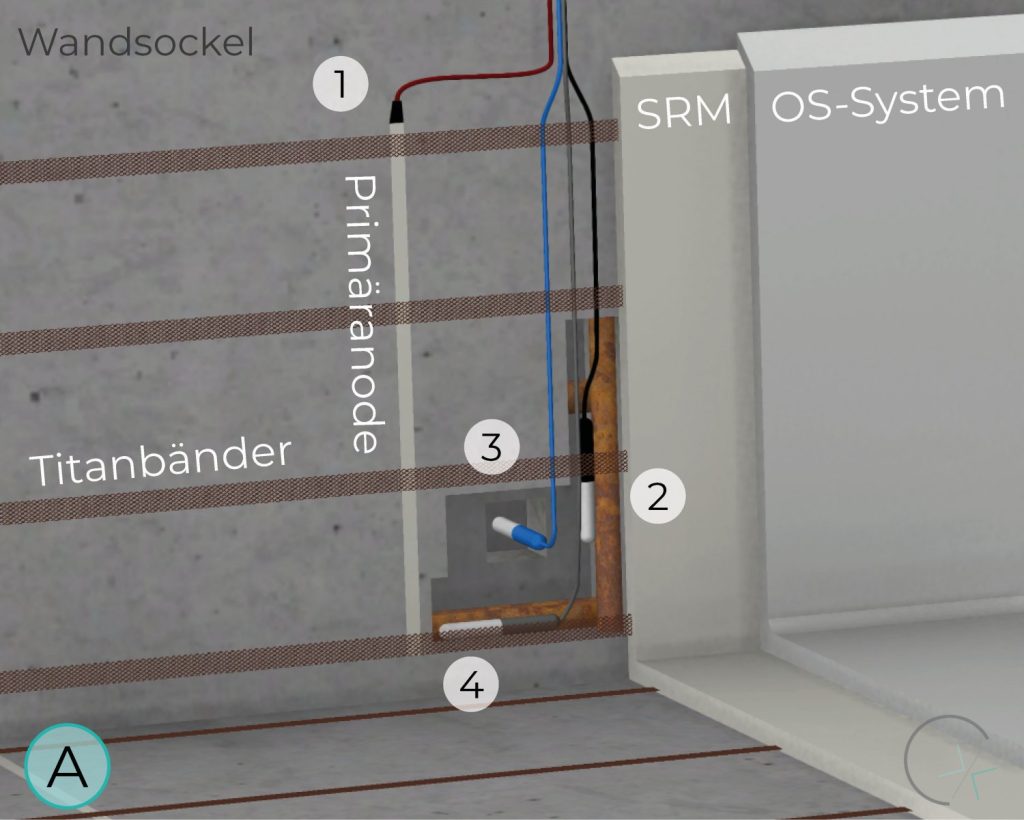
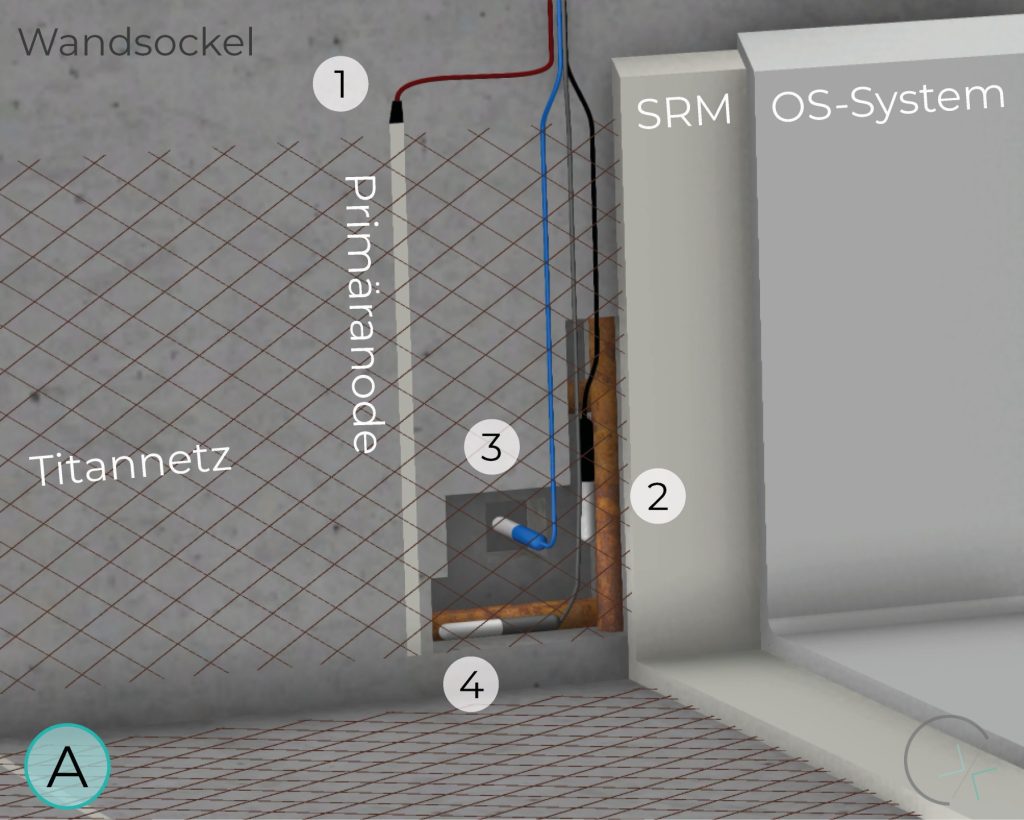
WALL BASE
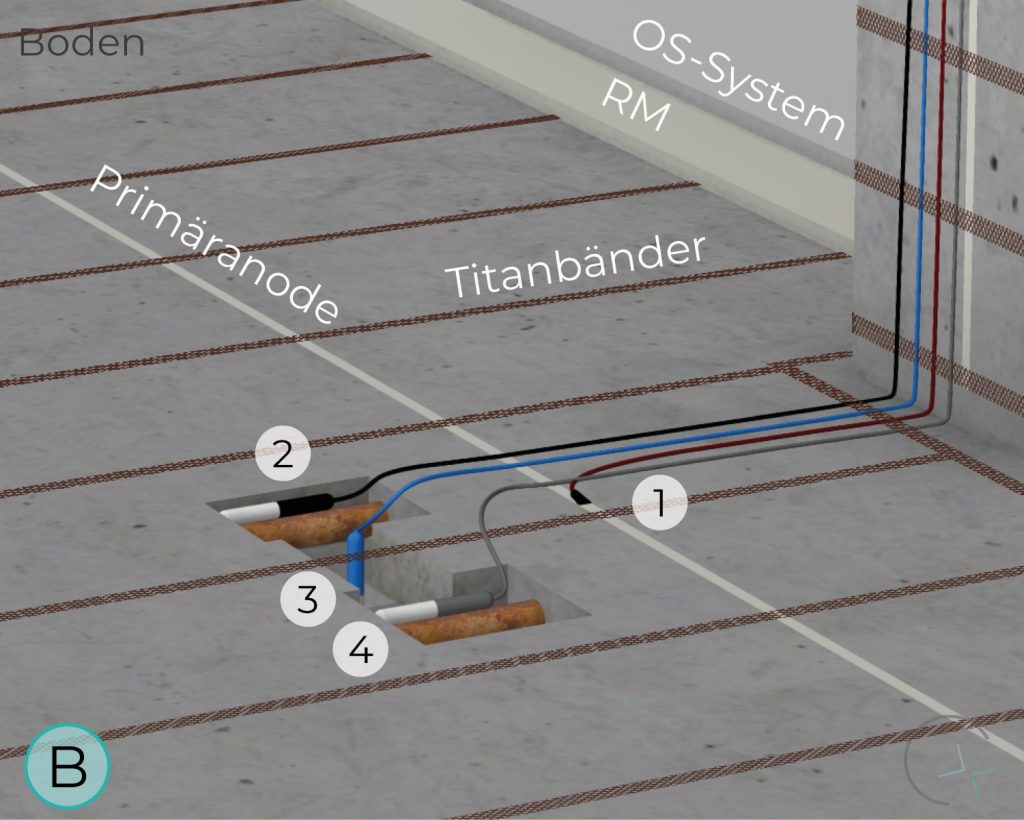
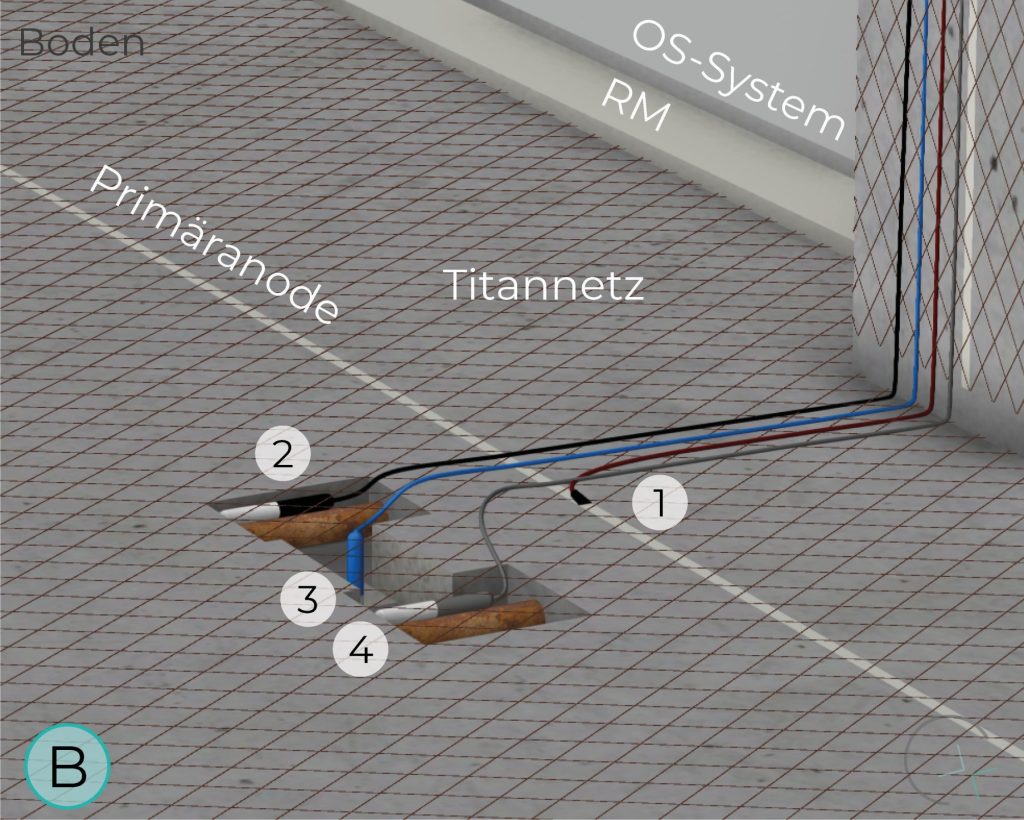
FLOOR
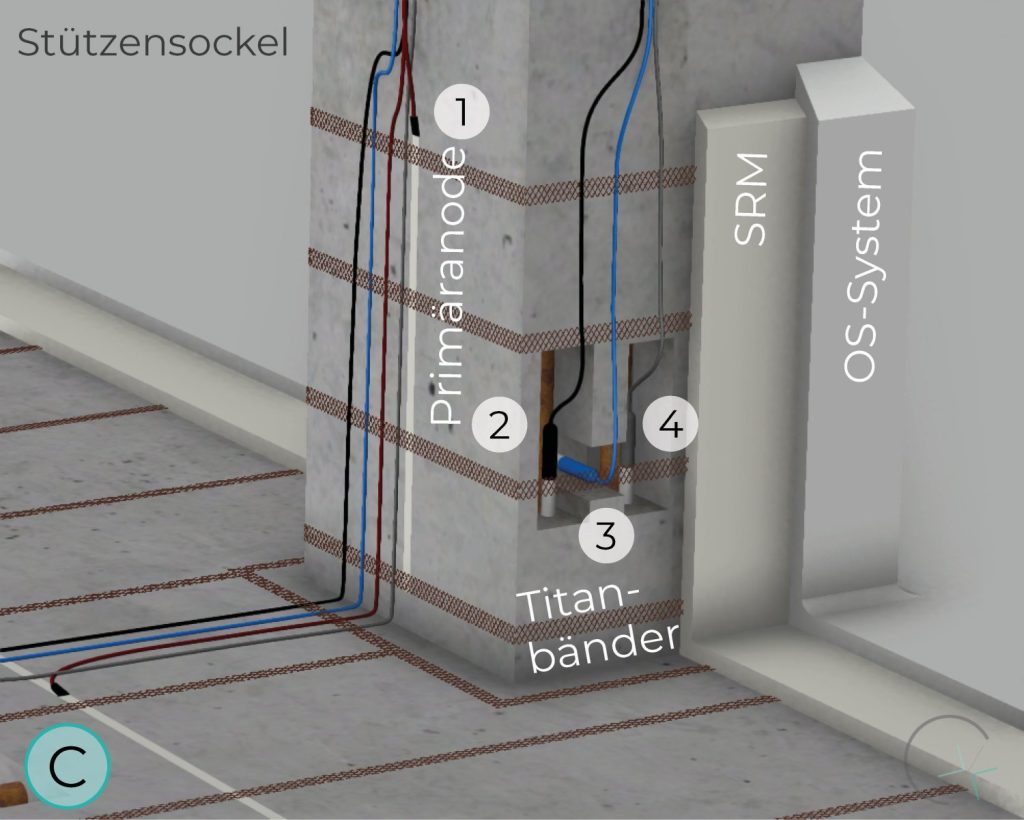
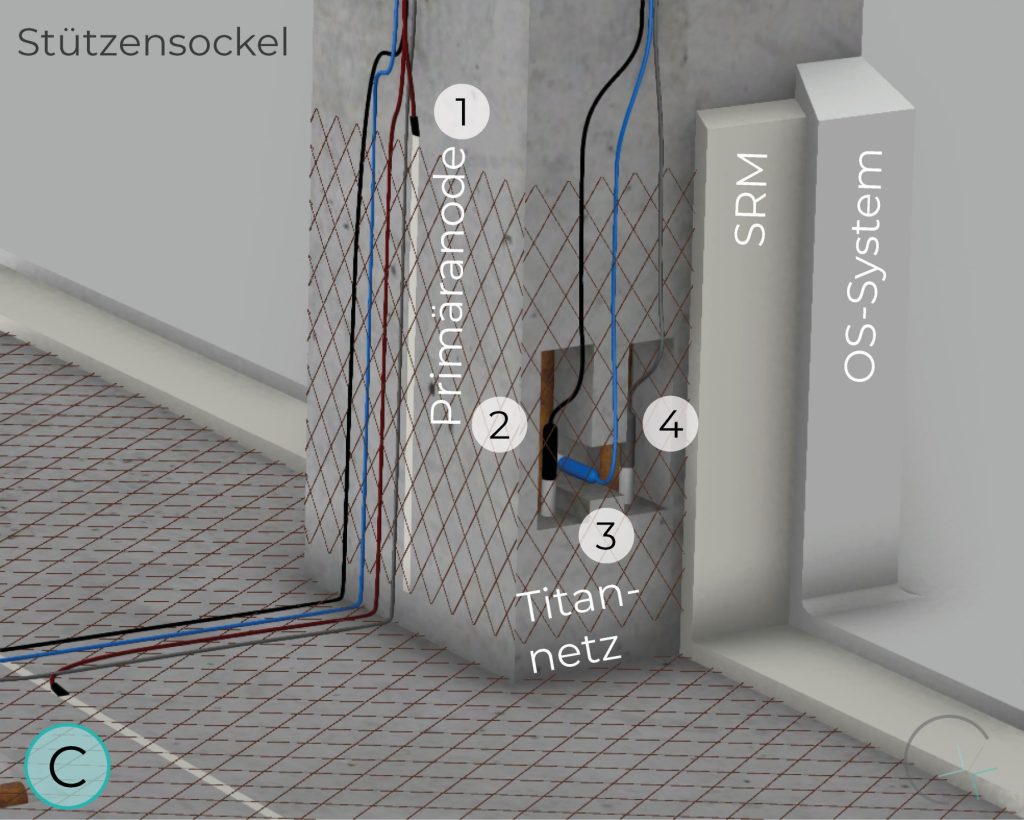
PILLAR BASE
Ti/MMO mesh anodes, available in various mesh sizes and corresponding power capacities, can be applied to different structural components. When designed properly, their geometry allows for optimal current distribution.
In 2004, the second multi-storey car park in Germany was rehabilitated using cathodic protection (CP). The column bases were protected using titanium ribbon and mesh anodes. The system is still in operation today. More information can be found in our project portfolio.
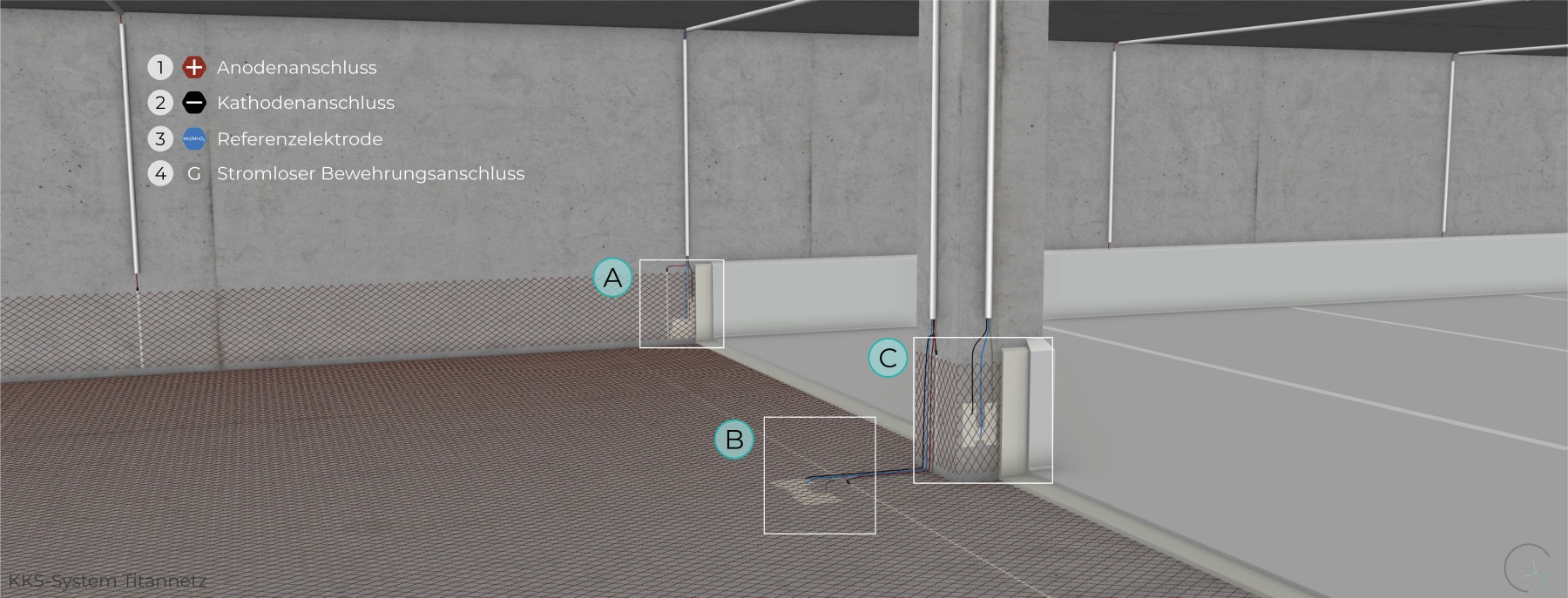

WALL BASE
FLOOR
PILLAR BASE
Ti/MMO anodes in the form of discrete units, available in different configurations and power capacities, are ideal for hard-to-reach structural components such as construction joints or consoles. This type of anode poses unique design and implementation challenges.
The second and third installations of cathodic protection systems for multi-storey car parks in Germany were completed in 2004/2005. Discrete anodes were used to protect columns and support consoles.
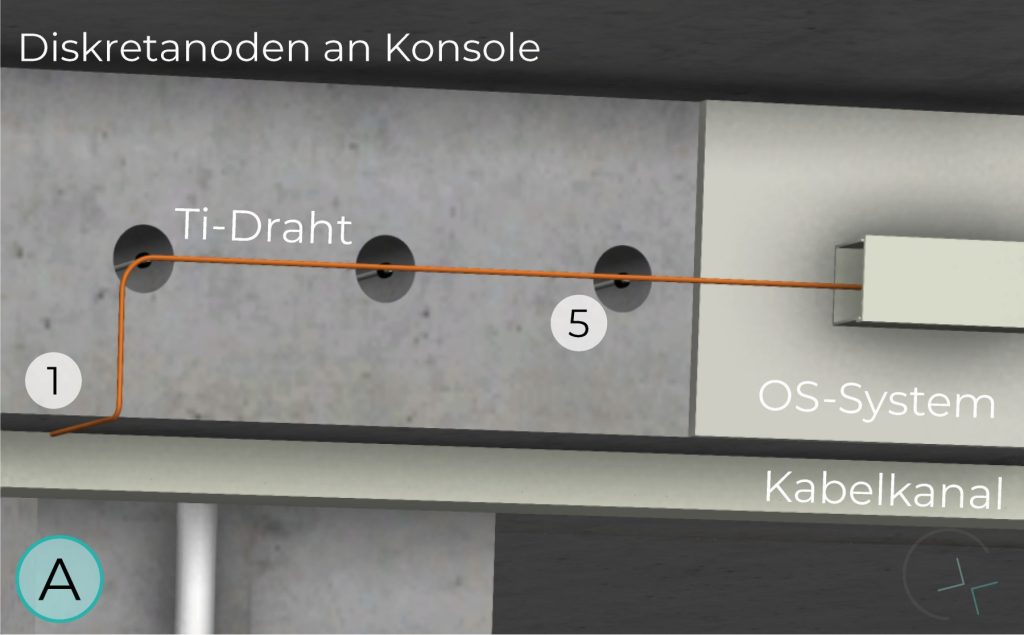
CONSOLE
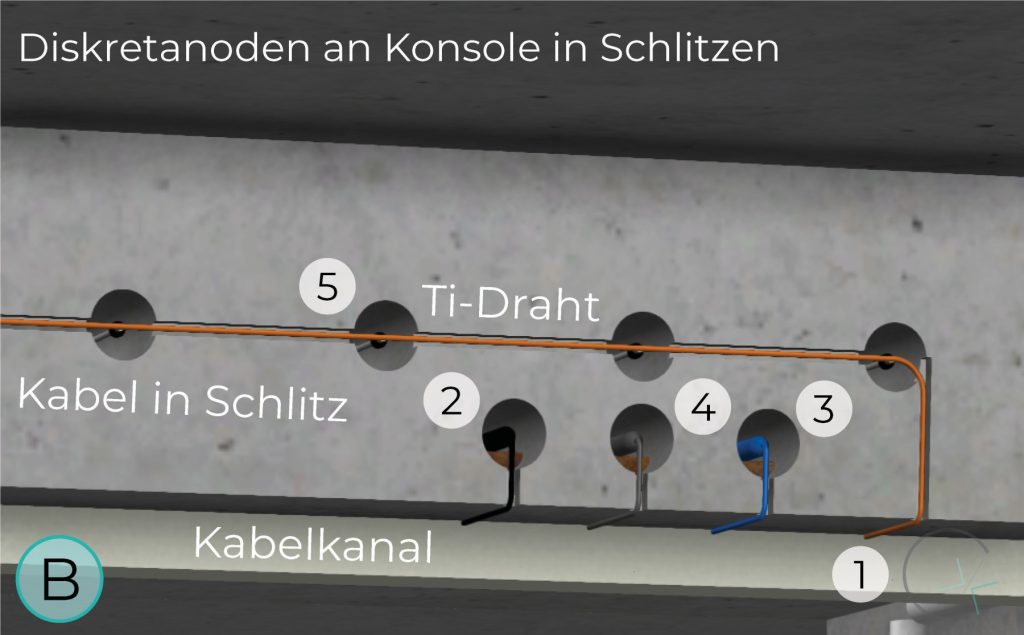
CONSOLE IN SLOTS
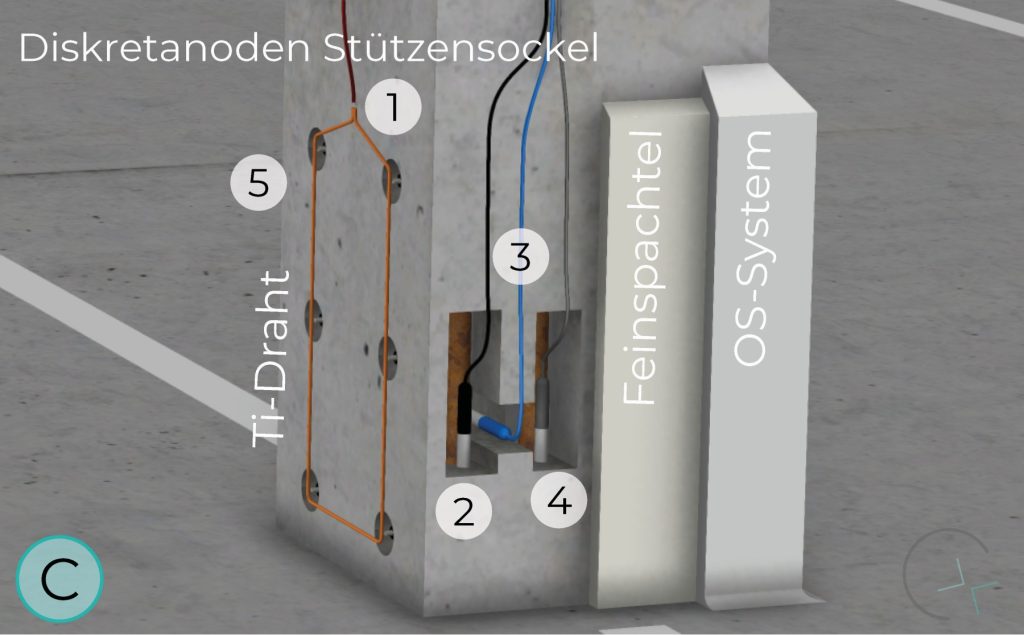
POST BASE
The conductive coating system, combined with the appropriate surface protection system, which serves as a crucial functional component for corrosion protection, can be used as an alternative to Ti/MMO anodes in various structures. This type of anode is a niche solution suitable for several specific applications.
The life span depends significantly on the precise design, careful implementation, and ongoing maintenance.
The first CP application was in 2000 on a balcony in Jüchen, where a conductive coating served as the anode system.
The first use of this kind of system in a parking garage in Germany was in 2002, where ceiling surfaces were protected. The system is still in use today. More information can be found in our project portfolio.
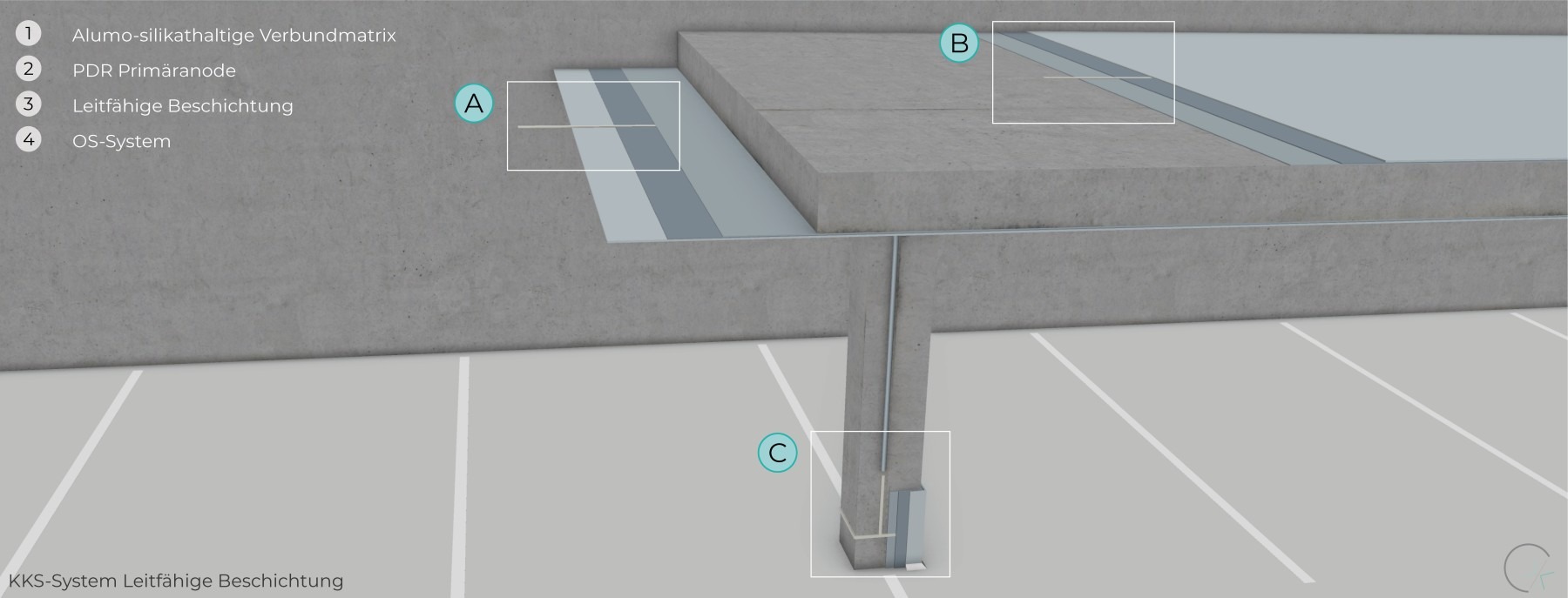
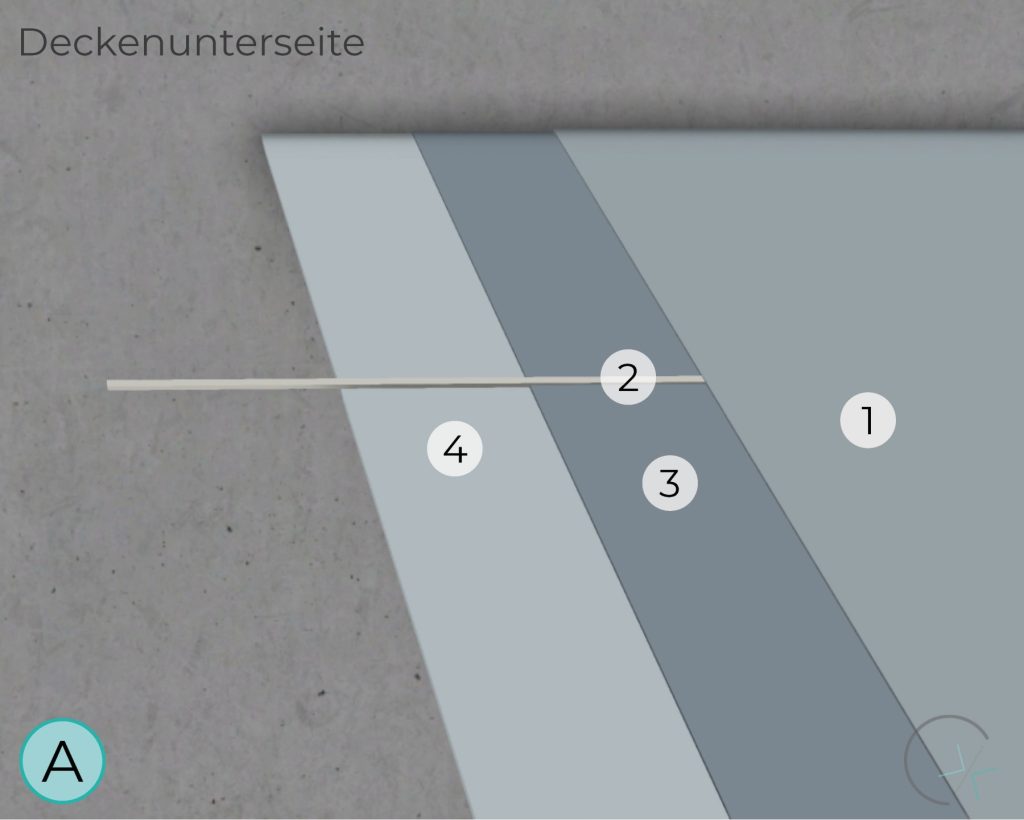
BOTTOM OF CEILING
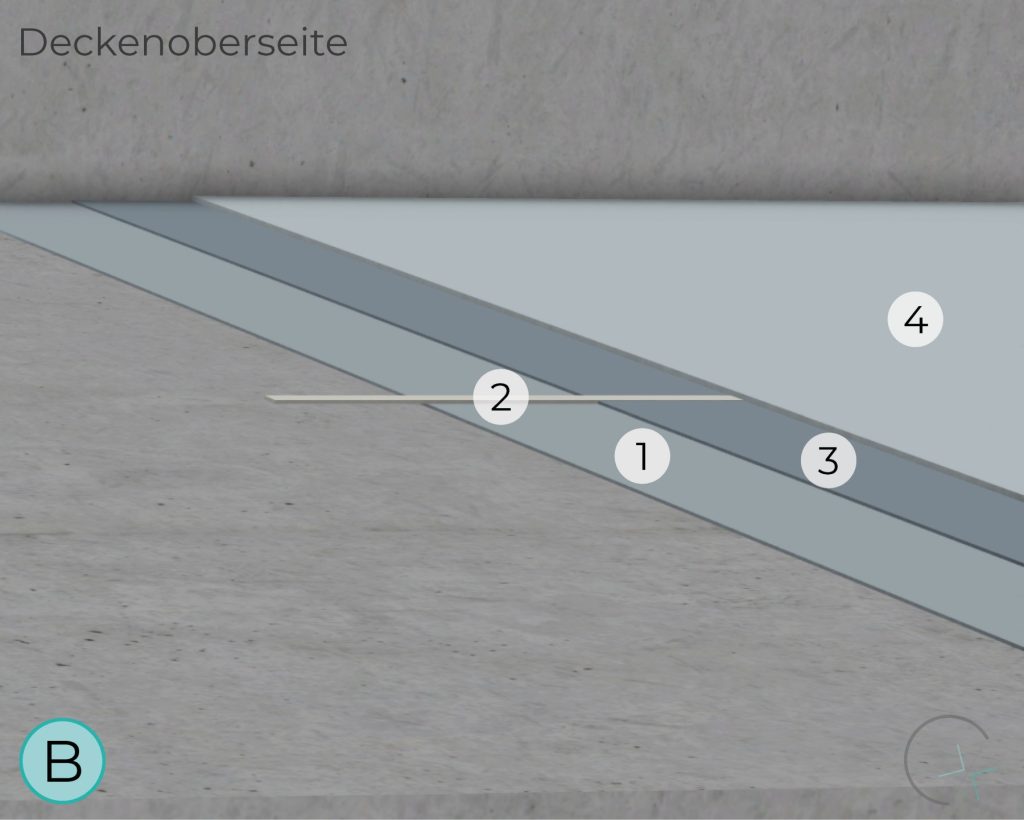
TOP OF CEILING
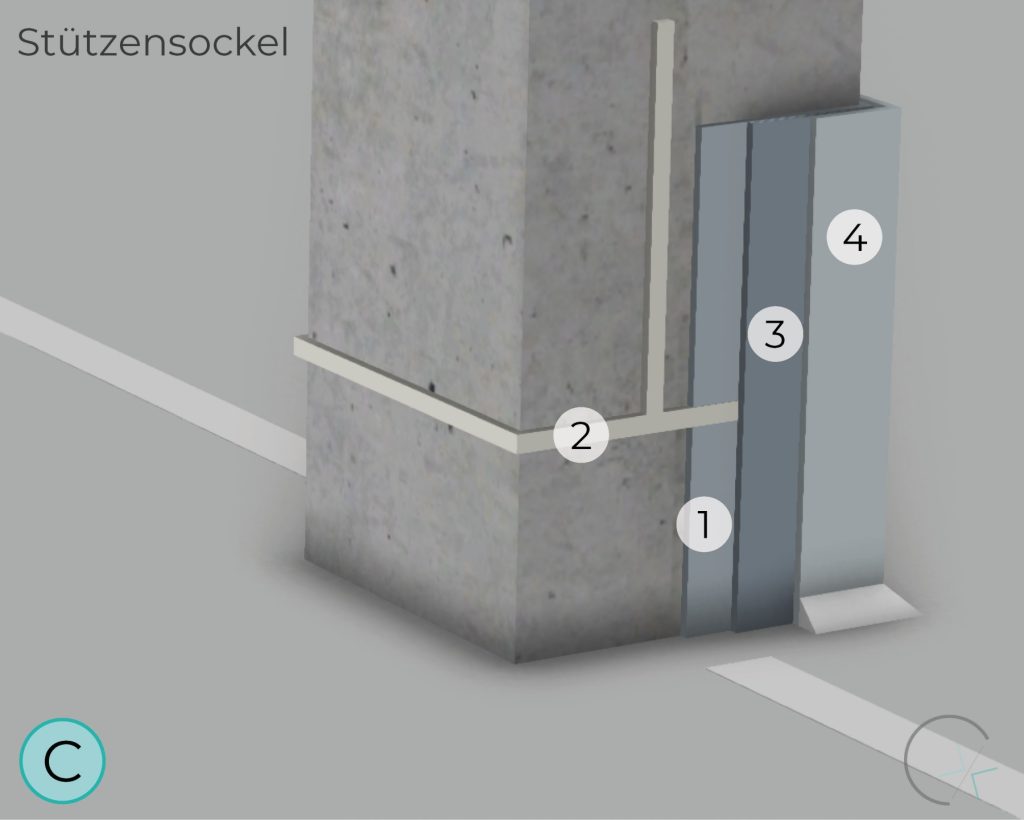
POST BASE
The zinc mesh anode, activated through a special embedding mortar, can be applied in various areas. As a niche anode system, it is suitable for specific applications.
Thorough preliminary investigation, proper design, precise implementation, and continuous maintenance are essential for the performance, usability, and application limits of this system.
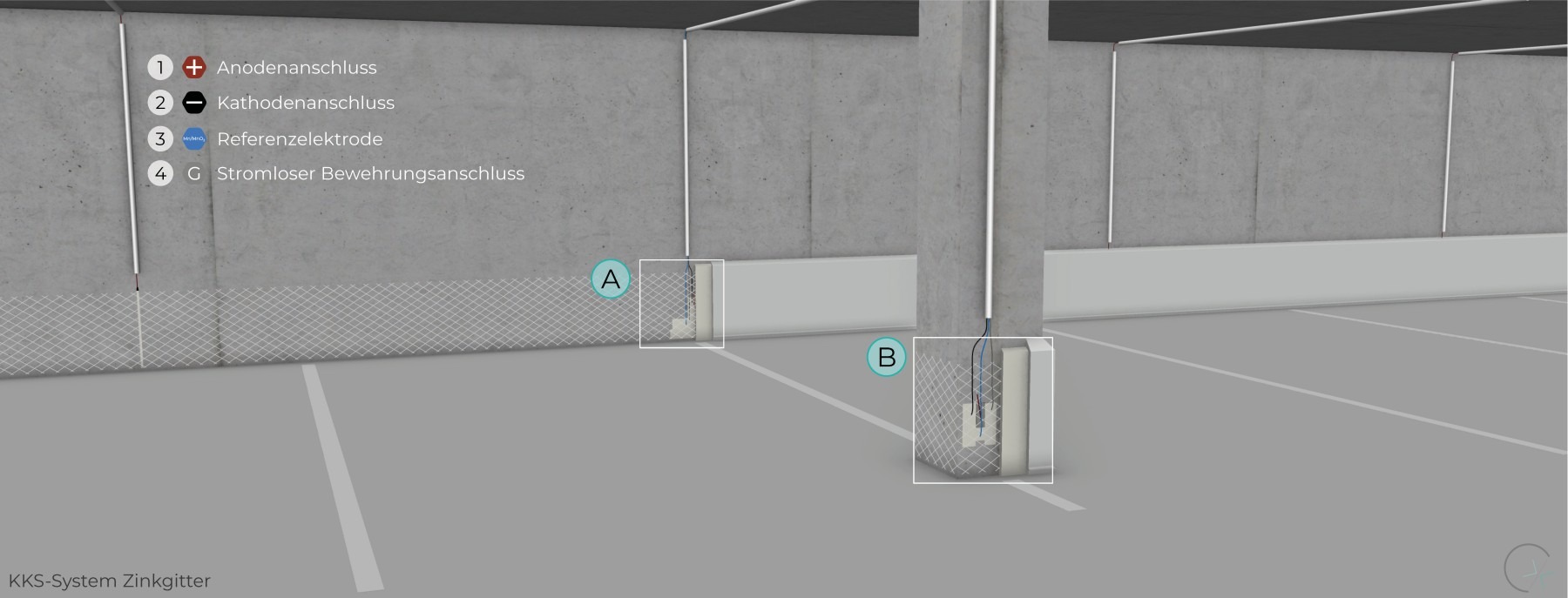
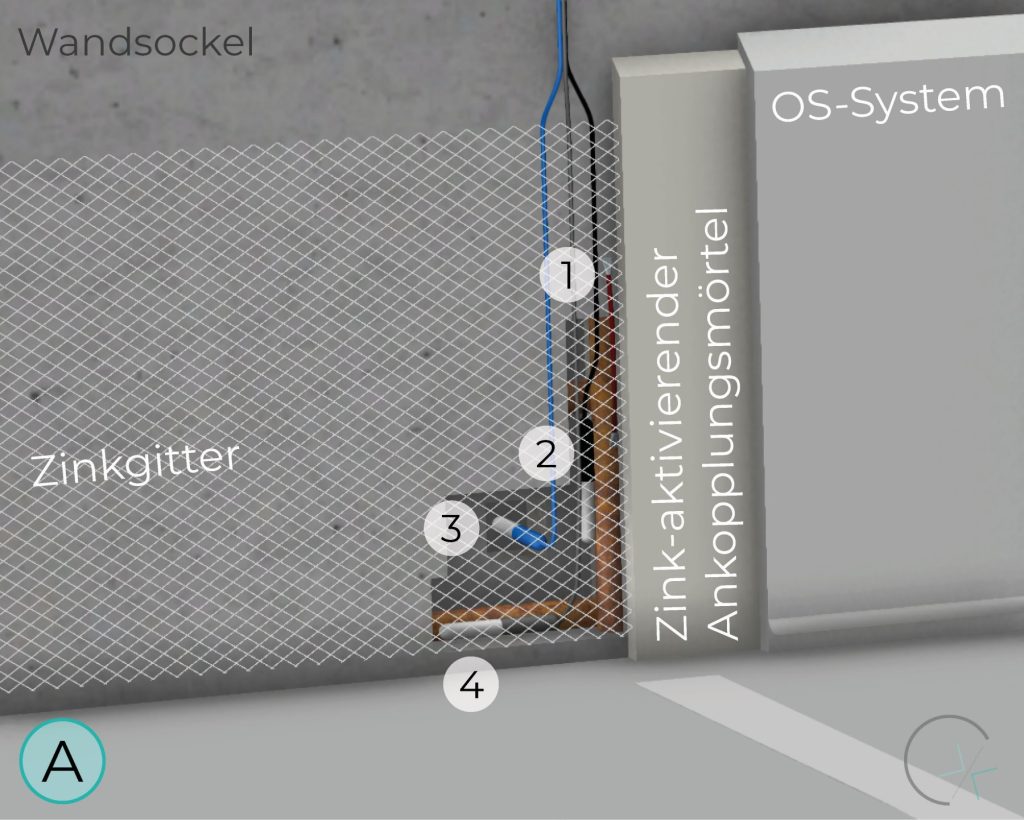
WALL BASE
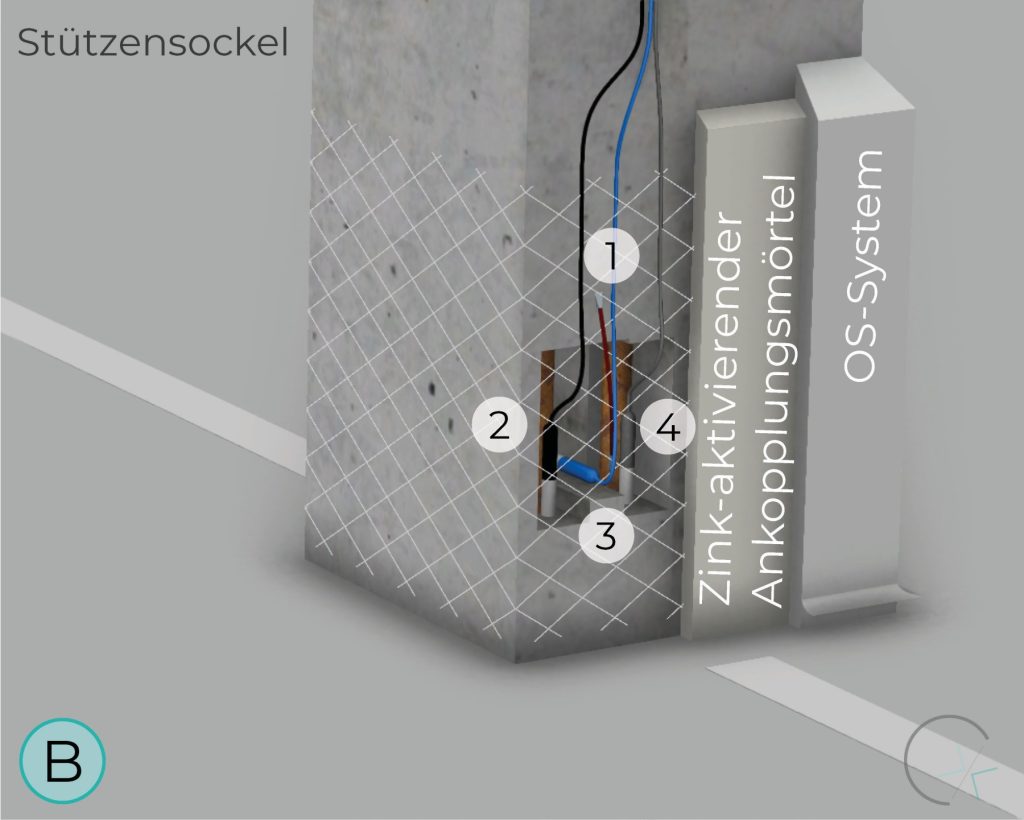
POST BASE
Monitoring-System
Intelligente Monitoring-Systeme bieten vielfältige Einsatzmöglichkeiten – sowohl präventiv im Neubau zur frühzeitigen Erkennung potenzieller Schädigungen als auch im Bestand zur Überwachung bereits vorhandener Schäden.
Zunehmend kommen sie auch als Nachweis- und Qualitätssicherungsinstrumente zum Einsatz, um den Erfolg elektrochemischer oder konventioneller Instandsetzungsverfahren zu bestätigen und zu dokumentieren.
Messgrößen wie Temperatur, elektrolytischer Widerstand, Makrostrom, Spannung, Feuchtigkeit und Strom können erfasst werden. Durch intelligente Sensor-Topologien lassen sich die Systeme flexibel an verschiedene Umgebungsbedingungen und Bauwerksstrukturen anpassen.
Mit Cloud-Anbindung avancieren Sie zum „gläsernen Auge“ des Bauwerks – transparent, kontinuierlich und vernetzt.
FAQ
What is cathodic protection?
Cathodic protection (CP) is a key method in structural repair, significantly extending the life span of reinforced concrete structures.
A controlled electrical current is applied to the reinforcement to slow down or entirely stop electrochemical corrosion processes.
Especially in chloride-contaminated or otherwise aggressive environments, CP offers effective protection against corrosion of the reinforcement in the concrete.
By polarizing the reinforcing steel to a stable electrochemical potential, the steel is effectively protected from further corrosion. The result: significantly lower repair costs and long-term preservation of structural integrity – for bridges, parking garages, and marine infrastructure.
To ensure lasting effectiveness, regular monitoring and maintenance are essential.
In summary, cathodic protection is a cost-effective, sustainable, and technically proven method to protect structures from progressive damage and costly consequences.
How does cathodic protection work?
Cathodic protection works by manipulating the electrochemical reaction that causes corrosion. This is done by making the metal to be protected the cathode of a galvanic cell. As a result, the metal’s oxidation is slowed or completely halted.
When is cathodic protection used?
Cathodic protection (CP) is used in a wide range of applications – particularly for repairing parking garage structures and other buildings exposed to corrosive environments.
In structural repair, CP is especially effective in the following cases:
- Concrete rehabilitation
Concrete structures often suffer damage from moisture, de-icing salts, and aggressive chemicals. Corroding reinforcement expands in volume, leading to cracks and spalling. CP interrupts or slows this process via targeted electrochemical methods, restoring structural integrity.
- Underground parking garages
Here, reinforcement is constantly exposed to moisture and chlorides (e.g., road salt). CP protects the reinforcement from ongoing corrosion and significantly extends the life of the structure.
- Bridges and tunnels
These structures face high corrosion risks due to weather, moisture, and chlorides. CP effectively protects the reinforcement and ensures long-term load-bearing capacity and safety.
What are the benefits of cathodic protection?
Advantages of cathodic protection for structures:
Long-term protection:
Structures like parking garages are often exposed to aggressive environments. CP offers lasting protection for reinforcing steel and significantly extends structural service life.
Preservation of structural integrity
Rebar corrosion leads to expansion, cracking, and spalling – compromising strength and safety. CP prevents this by stabilizing the reinforcement electrochemically.
Operation without interruption:
Unlike coatings or concrete removal, CP doesn’t require structures to be taken temporarily out of service. Systems can be installed and operated while the facility remains in use.
Effective in harsh environments
CP performs reliably under high chloride loads or persistent moisture – where conventional protection fails.
Cost-efficiency and sustainability
Though the initial cost may be higher, reduced repair frequency and damage costs quickly offset it. CP also conserves resources by preserving existing structures.